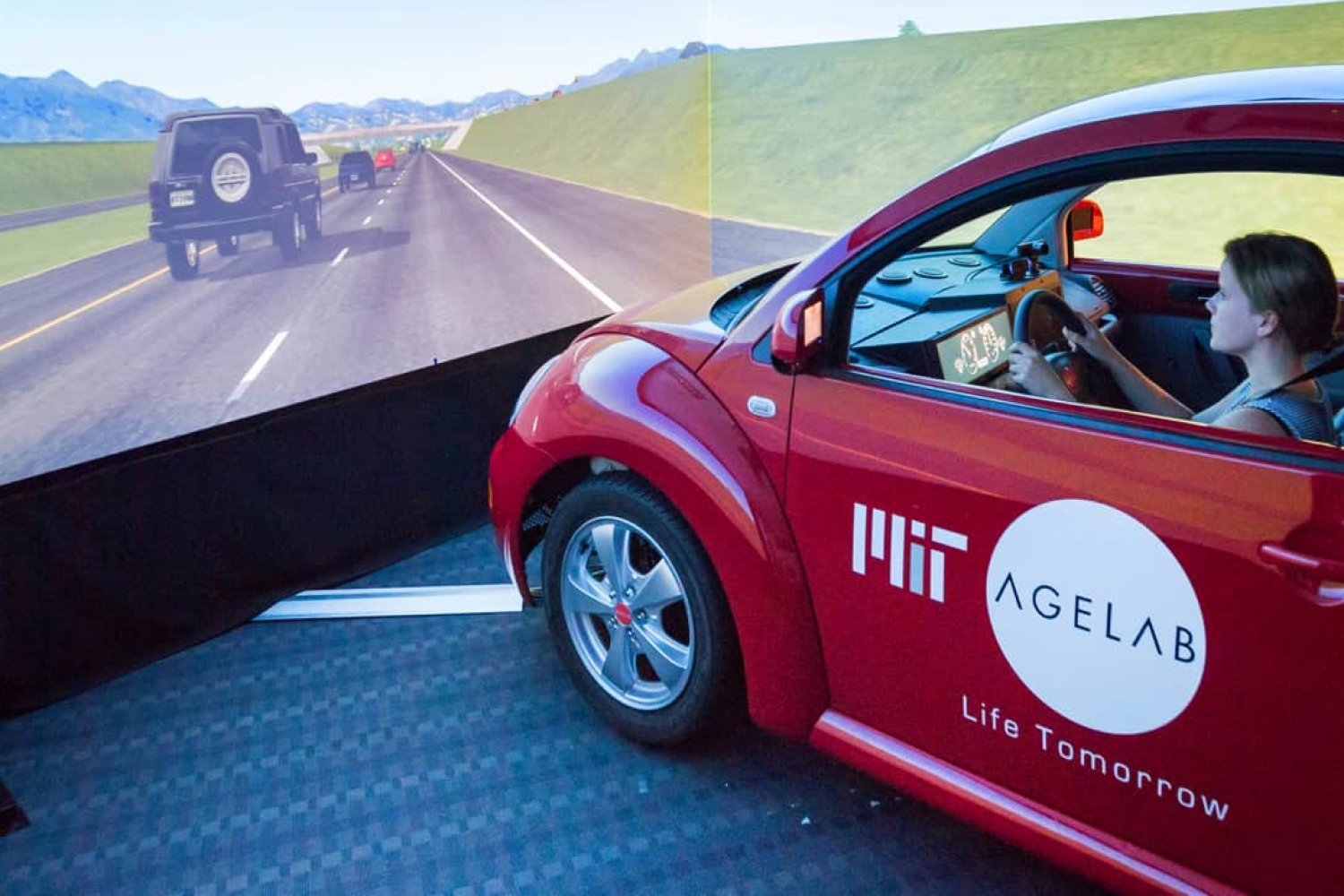
 MIT-Toyota collaboration powers driver assistance in millions of vehiclesA decade-plus alliance between MIT’s AgeLab and Toyota’s Collaborative Safety Research Center is recognized as a key contributor to advancements in automotive safety and human-machine interaction.
MIT-Toyota collaboration powers driver assistance in millions of vehiclesA decade-plus alliance between MIT’s AgeLab and Toyota’s Collaborative Safety Research Center is recognized as a key contributor to advancements in automotive safety and human-machine interaction. MIT engineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industriesTheir system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.
MIT engineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industriesTheir system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.
- MIT-Toyota collaboration powers driver assistance in millions of vehiclesA decade-plus alliance between MIT’s AgeLab and Toyota’s Collaborative Safety Research Center is recognized as a key contributor to advancements in automotive safety and human-machine interaction.

- MIT engineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industriesTheir system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.

- Why some quantum materials stall while others scaleIn a new study, MIT researchers evaluated quantum materials’ potential for scalable commercial success — and identified promising candidates.
- Earthquake damage at deeper depths occurs long after initial activityWhile the Earth’s upper crust recovers quickly from seismic activity, new research finds the mid-crust recovers much more slowly, if at all.

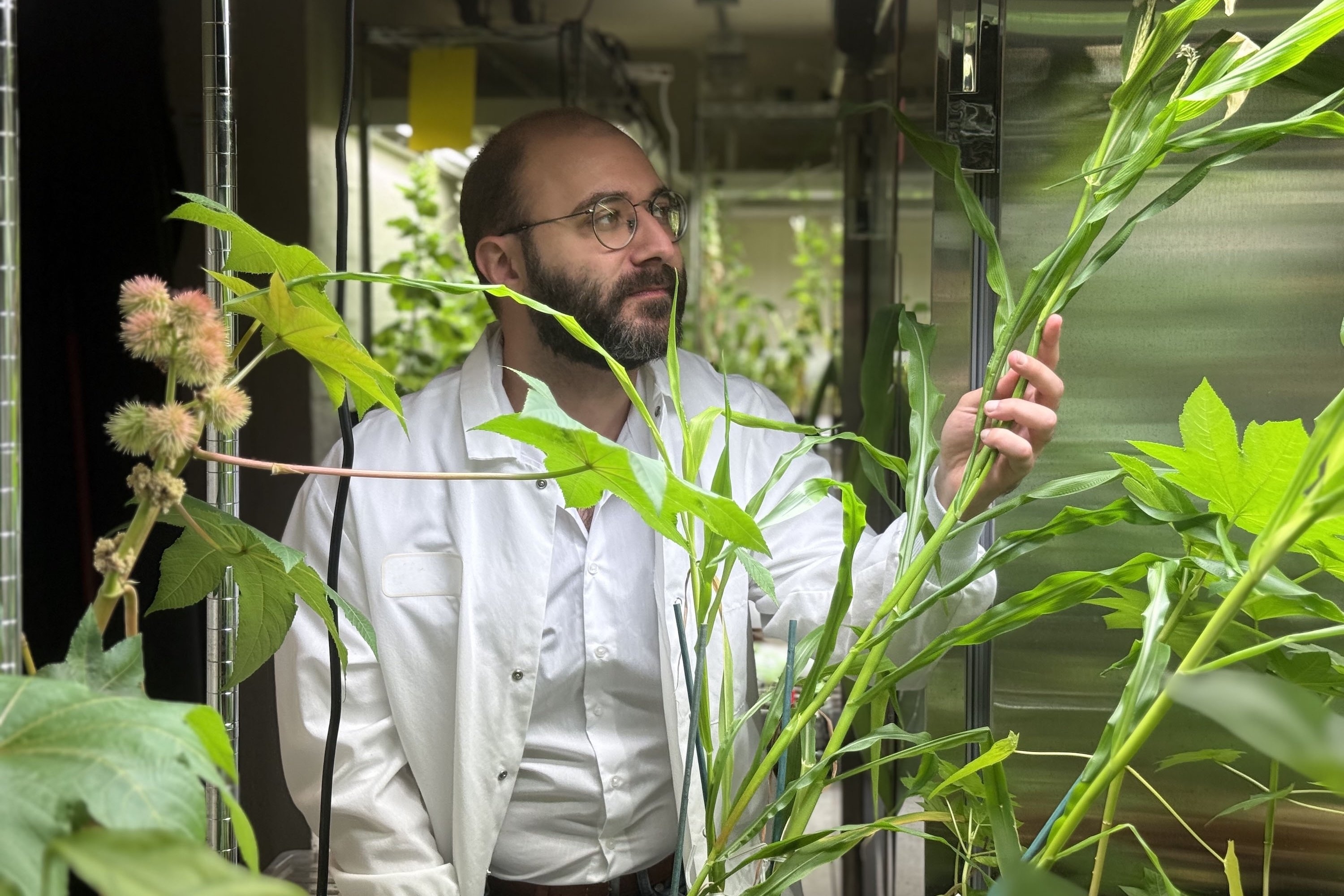
- Engineering next-generation fertilizersMIT postdoc Giorgio Rizzo harnesses plant chemistry to design sustainable fertilizers that could reshape modern farming.

- Optimizing food subsidies: Applying digital platforms to maximize nutritionAn algorithm can change the face of food assistance policy in the Global South, says MIT assistant professor and J-WAFS researcher Ali Aouad.

- Checking the quality of materials just got easier with a new AI toolActing as a “virtual spectrometer,” SpectroGen generates spectroscopic data in any modality, such as X-ray or infrared, to quickly assess a material’s quality.
- Helping scientists run complex data analyses without writing codeCo-founded by an MIT alumnus, Watershed Bio offers researchers who aren’t software engineers a way to run large-scale analyses to accelerate biology.
- New MIT initiative seeks to transform rare brain disorders researchThe Rare Brain Disorders Nexus aims to accelerate the development of novel therapies for a spectrum of uncommon brain diseases.

- Geologists discover the first evidence of 4.5-billion-year-old “proto Earth”Materials from ancient rocks could reveal conditions in the early solar system that shaped the early Earth and other planets.

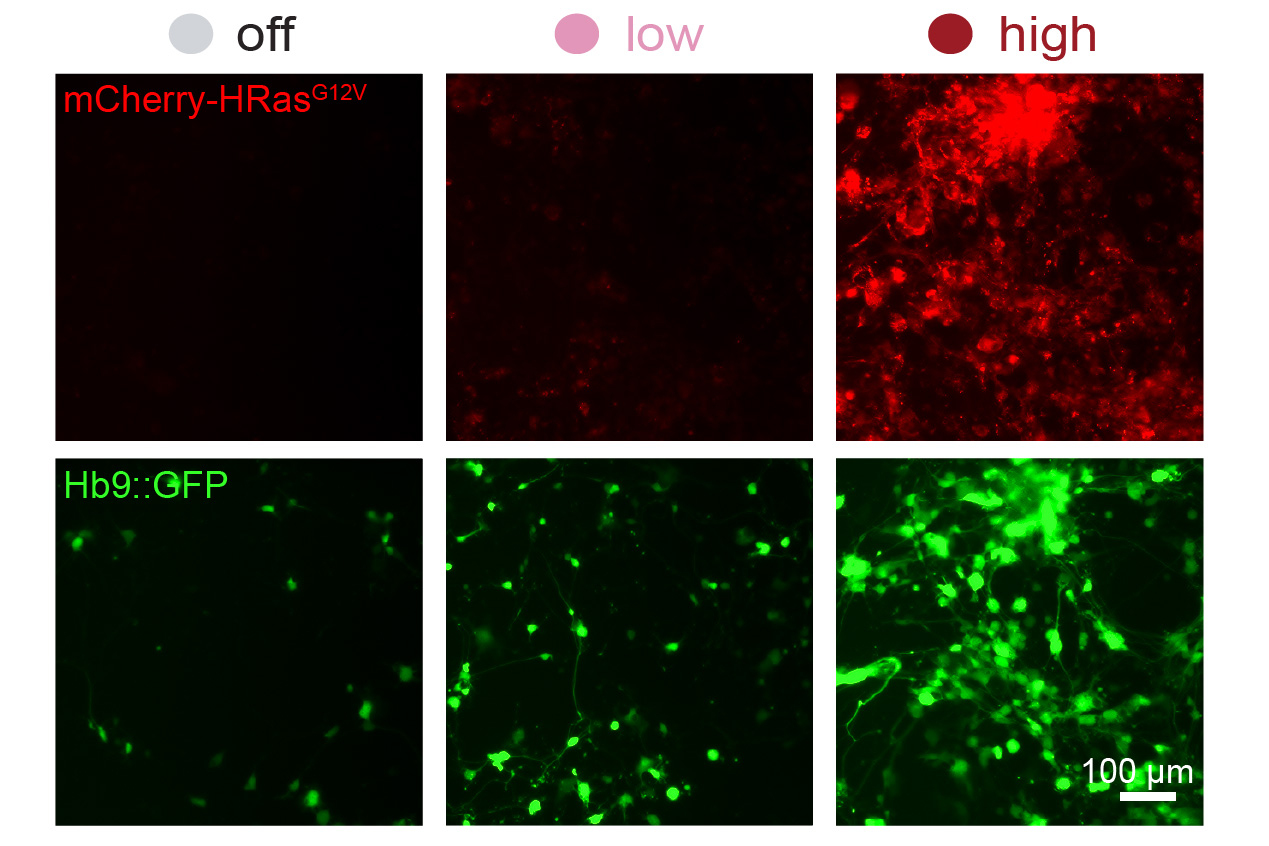
- A new system can dial expression of synthetic genes up or downThe promoter editing system could be used to fine-tune gene therapy or to more efficiently reprogram cells for therapeutic use.
- MIT releases financials and endowment figures for 2025The Institute’s pooled investments returned 14.8 percent last year; endowment stands at $27.4 billion.

- Ray Kurzweil ’70 reinforces his optimism in tech progressReceiving the Robert A. Muh award, the technologist and author heralded a bright future for AI, breakthroughs in longevity, and more.

- Gene-Wei Li named associate head of the Department of BiologyThe associate professor aims to help the department continue to be a worldwide leader in education, biological sciences, and fundamental research.

- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing and MBZUAI launch international collaboration to shape the future of AIThe MIT–MBZUAI Collaborative Research Program will unite faculty and students from both institutions to advance AI and accelerate its use in pressing scientific and societal challenges.

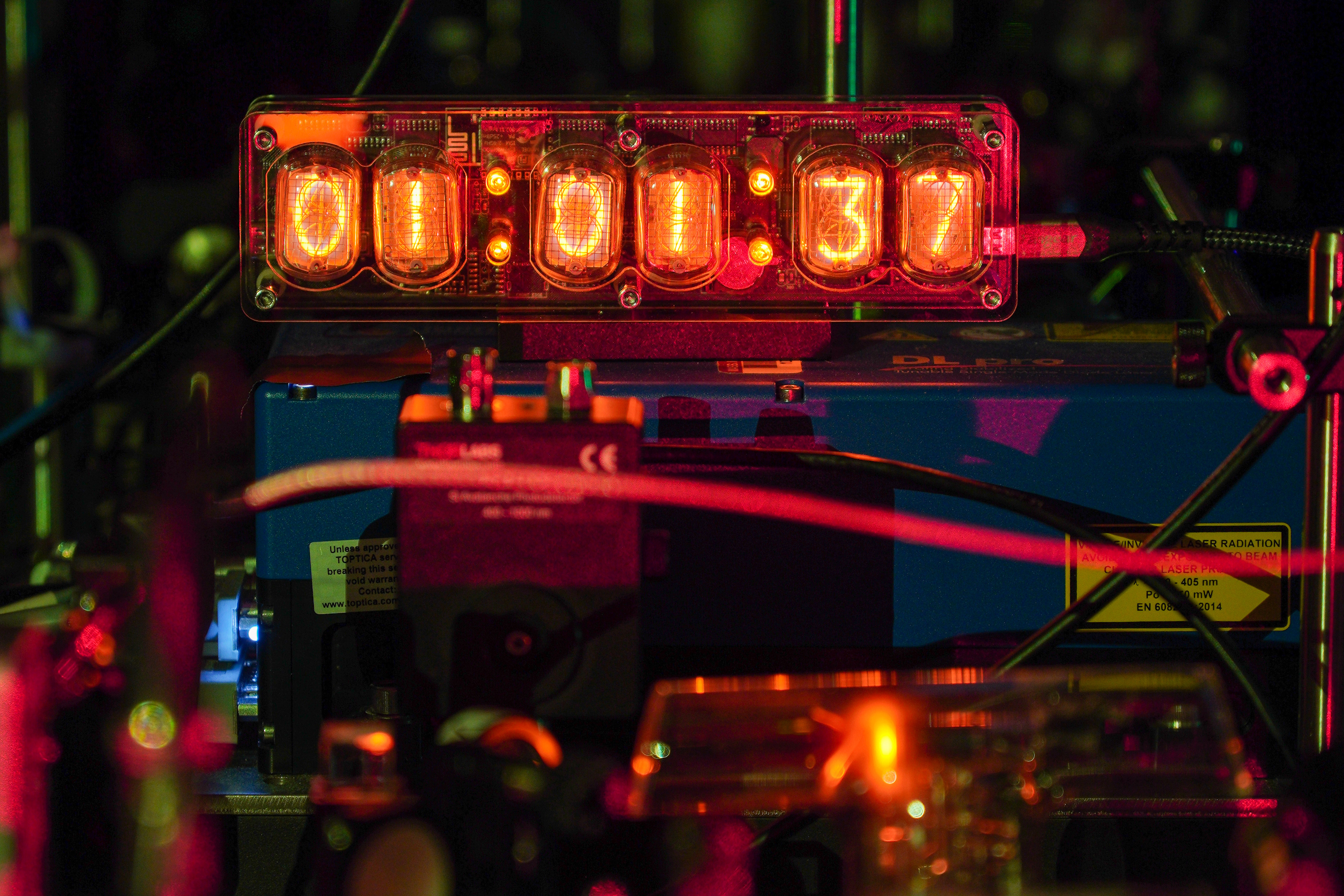
- MIT physicists improve the precision of atomic clocksA new method turns down quantum noise that obscures the “ticking” of atoms, and could enable stable, transportable atomic clocks.
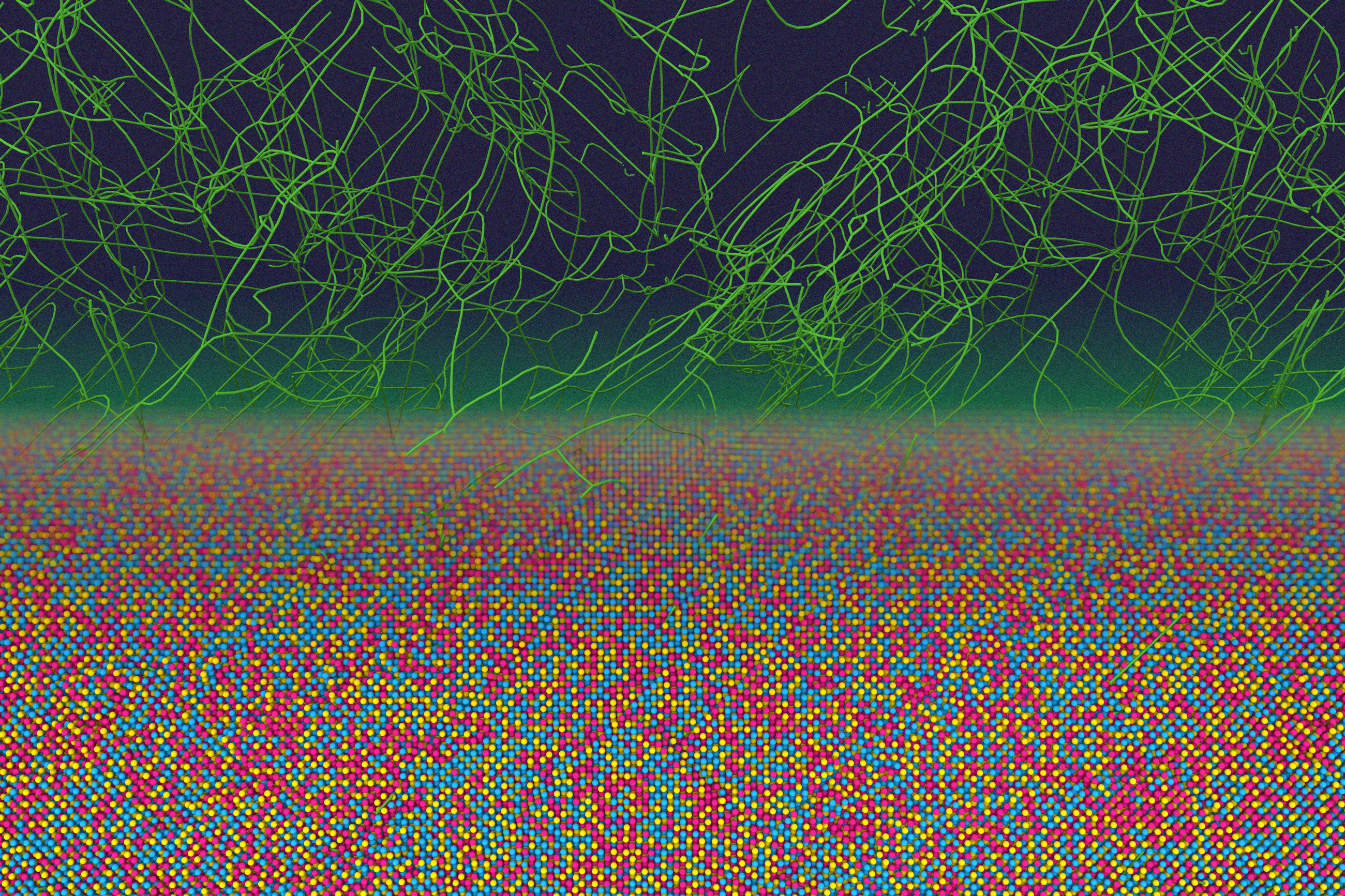
- Uncovering new physics in metals manufacturingMIT researchers discovered a hidden atomic order that persists in metals even after extreme processing.
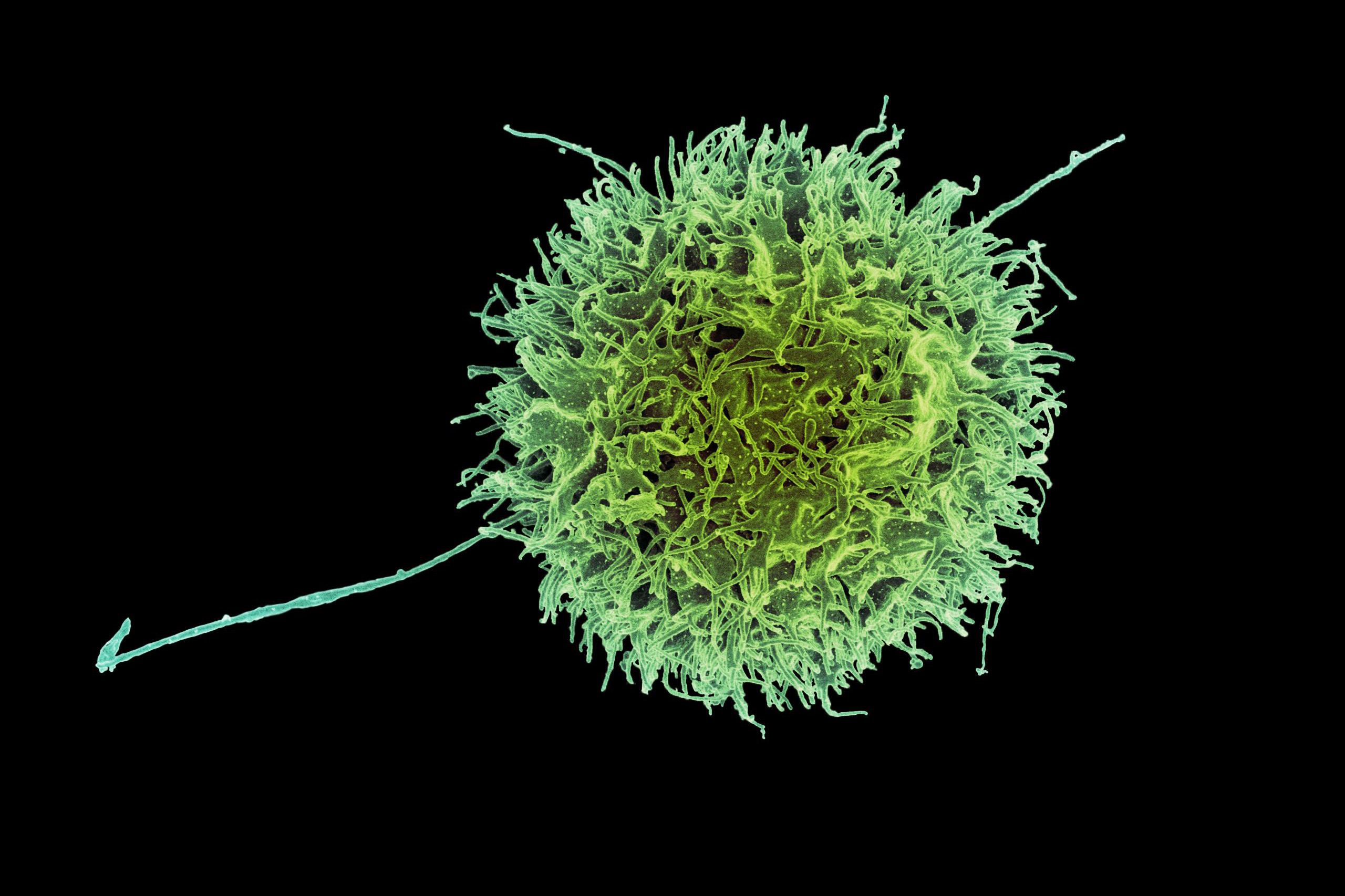
- Engineered “natural killer” cells could help fight cancerA new study identifies genetic modifications that make these immune cells, known as CAR-NK cells, more effective at destroying cancer cells.
- Laurent Demanet appointed co-director of MIT Center for Computational Science and EngineeringApplied mathematics professor will join fellow co-director Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou in leading the cross-cutting center.

- New prediction model could improve the reliability of fusion power plantsThe approach combines physics and machine learning to avoid damaging disruptions when powering down tokamak fusion machines.

Load more...
Loading...


