 Study shows mucus contains molecules that block Salmonella infectionMIT researchers now hope to develop synthetic versions of these molecules, which could be used to treat or prevent foodborne illnesses.
Study shows mucus contains molecules that block Salmonella infectionMIT researchers now hope to develop synthetic versions of these molecules, which could be used to treat or prevent foodborne illnesses. New AI system could accelerate clinical researchBy enabling rapid annotation of areas of interest in medical images, the tool can help scientists study new treatments or map disease progression.
New AI system could accelerate clinical researchBy enabling rapid annotation of areas of interest in medical images, the tool can help scientists study new treatments or map disease progression.
- Study shows mucus contains molecules that block Salmonella infectionMIT researchers now hope to develop synthetic versions of these molecules, which could be used to treat or prevent foodborne illnesses.

- New AI system could accelerate clinical researchBy enabling rapid annotation of areas of interest in medical images, the tool can help scientists study new treatments or map disease progression.

- Technique makes complex 3D printed parts more reliableNew research enables computer designs to incorporate the limitations of 3D printers, to better control materials’ performance in aerospace, medical, and other applications.

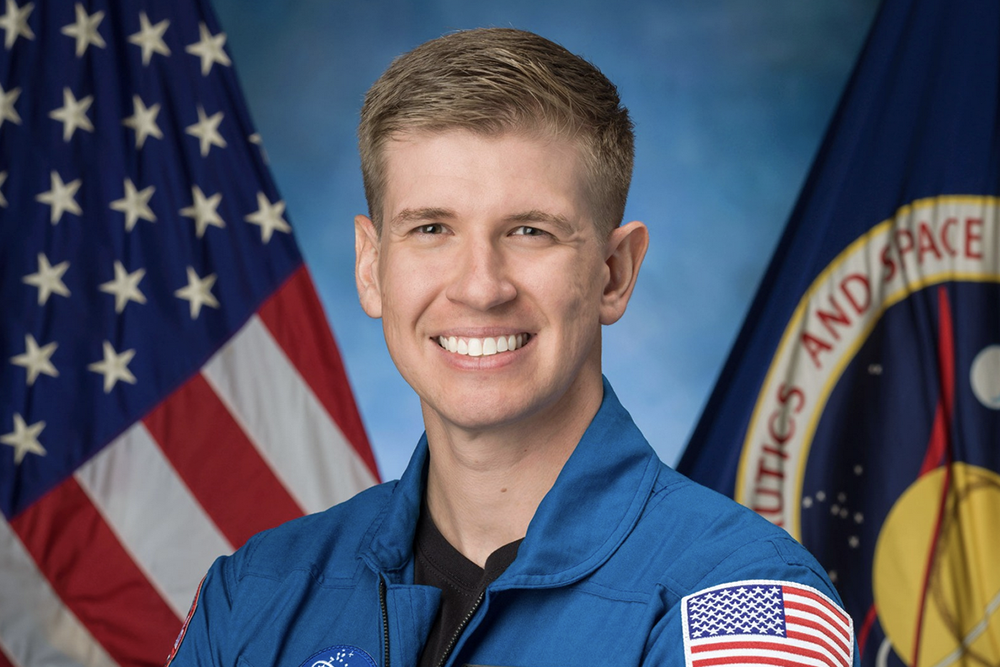
- NASA selects Adam Fuhrmann ’11 for astronaut trainingThe AeroAstro alumnus, who participated in Air Force ROTC and the Gordon Engineering Leadership Program at MIT, is a test pilot and one of 10 new astronaut candidates selected from around the nation.

- MIT engineers develop a magnetic transistor for more energy-efficient electronicsA new device concept opens the door to compact, high-performance transistors with built-in memory.

- MIT’s work with Idaho National Laboratory advances America’s nuclear industryThe collaboration has led to new fuels and a variety of other projects to enable clean, safe nuclear energy.
- MIT named No. 2 university by U.S. News for 2025-26Undergraduate engineering, computer science, and business programs are all No. 1.

- New tool makes generative AI models more likely to create breakthrough materialsWith SCIGEN, researchers can steer AI models to create materials with exotic properties for applications like quantum computing.
Loading...


